Clause of Confidentiality: A Guide to Protecting Business Secrets
A complete guide to the clause of confidentiality. Learn its key elements, see real-world examples, and discover how to draft and manage them with AI.
Tired of nonsense pricing of DocuSign?
Start taking digital signatures with BoloSign and save money.
A clause of confidentiality is a promise, baked right into a contract, to keep certain information under wraps. Think of it as a legal shield for your most valuable business secrets—everything from client lists and financial data to proprietary code and marketing strategies. It stops sensitive info from falling into the hands of competitors or the general public.
The Legal Backbone of Business Trust
In almost any business deal, you have to share something sensitive. Whether you're hiring a new executive, partnering with another company, or onboarding a client, information gets exchanged. It could be a proprietary software algorithm, a patient's medical history, or a sensitive client list.
A confidentiality clause is the legal backbone that makes these exchanges possible. It replaces wishful thinking with a clear, enforceable agreement.
Without it, you’re just running on trust—a risky game when your competitive advantage is on the line. Imagine a staffing agency in Canada that shares a top-tier candidate's resume with a client in the US. The confidentiality clause in their service agreement is what stops that client from simply cutting the agency out and hiring the candidate directly. This is where a reliable digital signing solution becomes critical to formalize the terms quickly.
Embedded Clause vs Standalone NDA
While both are designed to protect secrets, a confidentiality clause isn't the same as a standalone Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA). Knowing which one to use is crucial for getting the right protection.
- Embedded Confidentiality Clause: This is a section inside a larger agreement, like an employment contract or a master service agreement. It's perfect for ongoing relationships where keeping things quiet is just one of many important terms.
- Standalone NDA: This is a separate, dedicated contract with just one job: establishing confidentiality. It’s the go-to for preliminary talks—like exploring a potential merger, vetting a vendor, or interviewing a C-suite candidate before an official offer is on the table.
To help you decide, here’s a quick comparison.
| Aspect | Standalone NDA | Embedded Confidentiality Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Context | Pre-relationship or single-purpose discussions. | Part of a broader, ongoing business relationship. |
| Scope | Narrowly focused on protecting specific information for a defined purpose. | Integrated with other terms and conditions of the main contract. |
| Best For | M&A talks, vendor vetting, early-stage partnerships. | Employment, service agreements, joint ventures. |
| Document | A completely separate, self-contained agreement. | One section within a larger, multi-purpose contract. |
The main difference comes down to context. An NDA is a focused tool for a specific, often temporary, interaction. A confidentiality clause is woven into the fabric of a much larger business relationship, making it a critical piece of the overall puzzle. To see how this and other provisions work together, it helps to understand the core elements of a contract that make it legally sound.
Key Takeaway: Forgetting about confidentiality is like leaving your company’s digital front door wide open. A well-written clause prevents accidental leaks, discourages bad actors, and gives you a clear legal path forward if a breach happens—saving you from lost revenue, ugly legal fights, and a damaged reputation.
The Real Risks of a Data Leak
A breach of confidentiality is far more than just an awkward moment. It can have crippling consequences.
Imagine a logistics company whose confidential shipping routes and pricing models get leaked to a rival. The immediate fallout is a lost competitive edge, potentially dragging them into a price war they can’t afford to win.
Or think about a consultant who accidentally shares one client's strategic plans with another. They're not just facing a lawsuit; their professional reputation could be damaged beyond repair. These real-world scenarios show why a strong, enforceable confidentiality clause isn’t just legal filler—it's an essential shield for your business.
The Essential Elements of an Ironclad Confidentiality Clause
A confidentiality clause isn’t just a block of legal text; it’s a carefully constructed mechanism designed to protect your most sensitive information. To be effective and hold up under scrutiny, it needs a solid anatomy. Think of it like a security system—each component plays a critical role in keeping your assets safe.
This diagram shows how these protections can be structured, either as part of a larger agreement or as a standalone document.
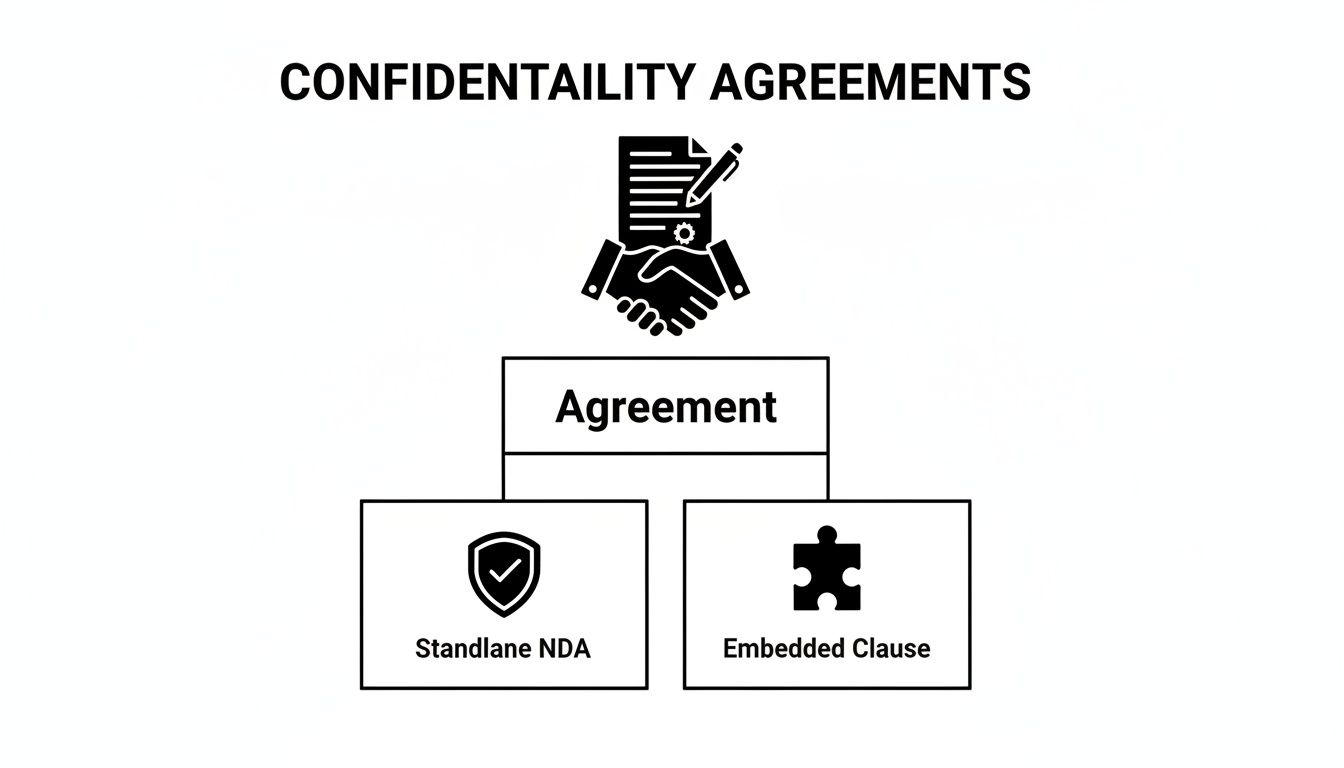
As you can see, your strategy can be flexible. You might use a dedicated NDA for a specific, high-stakes discussion or embed a clause into a larger commercial contract for an ongoing relationship. Understanding these core components is the first step toward building a clause that actually works.
Defining Confidential Information
This is the heart of your clause. It explicitly states what information is protected. A vague definition like "all business information" is a classic mistake and is often unenforceable in court. You need to be specific without being so narrow that you leave valuable data unprotected.
For a healthcare provider in Australia, this would include patient records and proprietary treatment protocols. For a real estate agency in the UAE, it would cover client financial statements and unlisted property details. The goal is to draw a clear, defensible line around what cannot be shared.
A well-drafted clause often includes specific categories, such as:
- Financial data and internal projections
- Customer lists and supplier details
- Marketing strategies and future business plans
- Proprietary software, source code, and trade secrets
- Sensitive employee and personnel information
Getting this definition right is a delicate balance. It needs to be broad enough to cover all critical assets but specific enough for a court to recognize and enforce. Our guide on how to write a contract explores how clear definitions form the bedrock of any strong legal agreement.
Scope of Obligations and Duration
Once you’ve defined what is confidential, the next step is to outline how it must be protected. This section details the receiving party's duties. It typically prohibits disclosing, copying, or using the information for any purpose other than the one specified in the agreement.
For instance, a logistics company sharing its route optimization data with a software vendor would restrict that vendor from using the data for anything other than developing the contracted software. Simple, but critical.
The duration specifies how long these obligations last. A common mistake is making the term indefinite for all types of information. The timeframe should be reasonable and often tied to how long the information remains valuable. While true trade secrets might be protected indefinitely, something like a marketing plan may only need protection for 1-3 years before it becomes outdated.
Exclusions and Permitted Disclosures
Not all information can remain secret forever. This part of the clause of confidentiality carves out exceptions, which is crucial for making the agreement fair and legally sound. Information is typically excluded if it:
- Was already public knowledge before it was shared.
- Was already rightfully known by the receiving party.
- Is independently developed by the receiver without using the confidential information.
- Is disclosed with the disclosing party’s written permission.
The clause must also cover permitted disclosures, such as when a party is required by law or a court order to reveal information. A good clause will require the receiving party to give prompt notice before making such a disclosure, giving the owner a chance to seek a protective order from the court.
Remedies for a Breach
Finally, what happens if someone breaks their promise? This section spells out the consequences. It typically states that a breach would cause irreparable harm that cannot be fixed with money alone, giving the disclosing party the right to seek an injunction—a court order to stop the leak.
An injunction is a powerful tool because it can immediately halt the unauthorized use or disclosure of your information, preventing further damage while you pursue other legal options.
This part of the clause acts as a powerful deterrent. By clearly stating the legal and financial consequences, it makes all parties think twice before mishandling sensitive data. Using a tool with AI contract review capabilities, like BoloSign, can help you automatically check if your clauses contain these essential elements, reducing risk before you send a document for a digital signature.
How Confidentiality Clauses Work Across Industries
Confidentiality isn't a one-size-fits-all concept. A clause of confidentiality that works for a logistics firm would be dangerously inadequate for a healthcare provider. The definition of a "secret," the risks involved, and the regulatory minefield change dramatically from one sector to the next.
This is why tailoring your agreements to your specific industry isn't just good practice—it's essential. A generic clause pulled from the internet often misses the critical details that make it legally enforceable in your world.

Let's explore how these clauses adapt to the unique demands of different professional environments, transforming from a general promise into a highly specific shield.
Healthcare: Patient Data and HIPAA Compliance
In healthcare, confidentiality is directly tied to patient safety and strict federal law. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US sets the gold standard for protecting Protected Health Information (PHI). Because of this, a confidentiality clause in any healthcare contract—whether with an employee, a software vendor, or a billing service—must be explicitly HIPAA-compliant.
Here, ‘Confidential Information’ is laser-focused on things like:
- Patient medical records and treatment histories
- Billing information and insurance details
- Any personally identifiable information (PII) linked to a person's health status
A breach isn't just a contract violation; it's a federal offense with severe penalties. The clause must outline precise data handling protocols, breach notification procedures, and subcontractor obligations, making it one of the most rigorous examples you'll find.
Staffing and Professional Services: Protecting People and Plans
For staffing agencies and professional services firms, the most valuable assets are people and plans. Their confidential information includes candidate pipelines, client hiring strategies, salary benchmarks, and proprietary recruitment methods. The goal is simple: prevent consultants from walking away with a client list or stop candidates from being poached outside of the agreement.
A typical confidentiality clause in a staffing context will fiercely protect:
- Candidate Information: Resumes, contact details, and interview feedback.
- Client Information: Organizational charts, hiring needs, and billing rates.
- Business Processes: Unique sourcing techniques and proprietary databases.
This ensures the agency’s hard work and intellectual capital remain theirs. The clause prevents a client from bypassing the agency to hire a candidate directly and stops former employees from taking the entire candidate pool to a competitor.
Real Estate: Securing Sensitive Deal Information
In the high-stakes world of real estate, discretion is everything. Confidentiality clauses are crucial in everything from listing agreements to commercial lease negotiations. They protect sensitive financial data and strategic deal terms that, if leaked, could derail a transaction worth millions.
For example: A commercial real estate broker in New Zealand representing a major tech company looking for a new headquarters must ensure the search remains secret. A leak could cause property values in the target area to skyrocket overnight, making the deal far more expensive.
Confidential information in real estate includes client financial statements, property appraisal values before they go public, negotiation strategies, and the identities of buyers or tenants during sensitive talks. The clause ensures all parties—agents, buyers, sellers, and their advisors—maintain silence until the ink is dry.
BoloSign makes it easy to manage these industry-specific needs through contract automation. You can create and save templates for healthcare, staffing, or real estate, ensuring every agreement you send has the right protections built-in. This powerful feature turns complex compliance into a simple, repeatable step, allowing you to sign PDFs online instantly.
Navigating Global Compliance and Data Privacy Laws
In our hyper-connected world, a simple handshake agreement to keep a secret just doesn’t cut it anymore. Your clause of confidentiality has a much bigger job to do than just protecting trade secrets; it has to navigate a tangled and ever-growing web of global data privacy laws. These regulations have completely reshaped the legal landscape, turning data protection from a "nice-to-have" into a mandatory, high-stakes game.
An agreement that ignores these rules isn't just weak—it's a direct ticket to staggering fines and a damaged reputation. Think of these laws as the universal rulebook for handling personal information. Your internal contracts are just one piece of the puzzle; they absolutely have to play by these external, non-negotiable rules.
The Global Privacy Mandate
The push for data privacy isn't a regional trend; it's a worldwide movement. As of early 2025, a stunning 144 countries have put data protection laws on the books, covering somewhere between 79% and 82% of the world's population. In the European Union, the GDPR is the undisputed gold standard, with regulators handing out €1.2 billion in fines in 2024 alone. Back in the U.S., 42% of states now have their own comprehensive privacy laws protecting 43% of Americans, each demanding strict confidentiality clauses to keep personal data safe. You can dive deeper into these global compliance trends from Encryption Consulting.
These laws fundamentally change how a clause of confidentiality must be written, especially when personal data is involved. They bring a whole new set of requirements that go far beyond a simple promise not to share.
Here are a few key mandates you'll often see:
- Data Processing Agreements (DPAs): Many regulations, like GDPR, demand a separate, detailed agreement if a third party—like a software vendor—is going to process personal data on your behalf.
- Breach Notification Rules: Your confidentiality clause has to line up with legal deadlines for telling people and authorities about a data breach, often within a tight window like 72 hours.
- Consumer Rights: The contract can't just override someone's legal right to access, correct, or delete their personal data.
- Data Transfer Restrictions: If you’re a global company, your confidentiality clauses need to address laws that limit moving personal data across borders.
Aligning Contracts with GDPR and eIDAS
For any business with a foothold in the European market, two regulations are absolutely critical: the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services (eIDAS) regulation. GDPR sets the rules for how personal data is collected, stored, and used, insisting that confidentiality agreements spell out these protections in detail. When you're working on global compliance, knowing the specifics—like how to manage a GDPR register of processing activities—is crucial. This guide to building an actionable Registre RGPD breaks it down nicely.
At the same time, eIDAS creates the legal foundation for electronic signatures across the EU, making sure that agreements signed digitally are legally binding. Any digital signing solution you use has to meet these standards to be valid.
Key Insight: Compliance isn't a "set it and forget it" task. Imagine a healthcare provider in Canada using a US-based software vendor to process patient data from the UAE. They need to draft a confidentiality agreement that respects the privacy laws of all three jurisdictions. This kind of complexity makes a robust, compliant platform essential.
This is exactly where a partner like BoloSign becomes indispensable. Our platform was designed from the ground up with global compliance in mind, supporting major regulations like eIDAS, ESIGN, GDPR, and HIPAA. When you create and send documents with BoloSign, you’re not just getting a signature; you’re using a system built to meet these tough international standards. Our AI-powered contract intelligence can help flag compliance risks before they become problems, while our secure eSignature process ensures every agreement is locked down with verifiable, legally sound authentication. By centralizing your agreements on a compliant platform, you dramatically lower the risk of costly legal penalties and protect the reputation you've worked so hard to build.
Common Pitfalls and Costly Mistakes to Avoid
A poorly drafted clause of confidentiality can create a dangerous false sense of security. It leaves your business exposed precisely when you need protection the most. In some cases, a bad clause is even worse than no clause at all—if it gets challenged and thrown out in court, you’ve just wasted time and money.
Spotting the common red flags and drafting errors is the first step toward creating an agreement that actually holds up under pressure. Many of these pitfalls come from language that’s either too vague or far too aggressive. Courts often refuse to enforce clauses they see as unreasonable or that unfairly stop someone from earning a living. The goal is to be protective, not prohibitive, and getting that balance right is everything.
Vague Definitions of Confidential Information
One of the most frequent—and fatal—flaws is using a lazy, overly broad definition for "Confidential Information." Phrases like "all business-related information" might sound like they cover everything, but legally, they’re often useless. A court needs specifics to enforce an agreement. If the definition is too vague, a judge might decide it’s impossible to know what was actually meant to be protected.
This ambiguity creates a massive loophole. A former employee or partner could easily argue they had no idea a certain piece of data was considered confidential because the clause never bothered to define it properly.
To avoid this, your clause should:
- List Specific Categories: Explicitly mention things like financial data, customer lists, marketing strategies, source code, and trade secrets.
- Use a Catch-All Phrase Carefully: After listing specifics, you can add a phrase like "...and any other information marked 'Confidential'." This adds a layer of flexibility without relying on pure ambiguity.
Unreasonable Timeframes and Scope
Another classic mistake is setting an indefinite or ridiculously long duration for the confidentiality obligation. While it’s tempting to demand secrecy forever, courts rarely enforce this, except for genuine trade secrets. They expect the timeframe to be tied to the useful life of the information. A marketing plan from five years ago likely has little value today, and a court won't enforce a lifetime ban on discussing it.
Similarly, the scope has to be reasonable. A clause that prevents a former salesperson from ever working in their industry again is a textbook example of overreach. The restrictions should be narrowly tailored to protect legitimate business interests, not to squash fair competition.
A strong confidentiality clause is precise. It clearly defines what is secret, for how long, and under what specific conditions, leaving no room for interpretation or legal challenges down the line.
Failing to Outline Practical Procedures
A great clause isn't just about what's forbidden; it's also about what's required. Many agreements fall flat because they don't spell out the practical steps for handling and returning confidential information. Your clause must clearly outline the procedure for returning or destroying all sensitive materials—both physical and digital—when a contract or employment ends.
This simple step prevents departing employees or partners from "accidentally" holding onto company data on their personal devices, which is an incredibly common source of data leaks. The consequences can be devastating. In the first half of 2025 alone, there were 1,732 publicly disclosed breaches, with the average cost in the U.S. hitting a record $10.22 million. You can find more details in the latest data privacy statistics from Usercentrics.
This is where an AI contract review tool becomes your best ally. A platform like BoloSign uses contract intelligence to automatically scan your agreements for these common pitfalls. It flags vague language, non-standard terms, and missing procedures, acting as your first line of defense. By catching these costly mistakes before a document goes out for an eSignature, you can secure your agreements and protect your business from entirely preventable disasters.
Streamline Your Agreements with Smart Contract Automation
Let's be honest, managing the nitty-gritty of a clause of confidentiality—from drafting and redlining to getting it signed and staying compliant—is often a slow, manual grind. It’s a process just begging for human error. But it doesn't have to be that way.
Modern tools are completely overhauling the agreement lifecycle. What was once a cumbersome, paper-chasing exercise can now be a fast, secure, and intelligent workflow. The trick is to stop thinking in terms of static documents and start embracing smart automation.
This shift frees up your legal, sales, and HR teams to focus on strategy instead of being buried in paperwork. By setting up standardized templates, automating the approval chain, and tracking everything in real-time, you can protect your most sensitive information with more speed and precision than ever before.
From Manual Effort to Automated Efficiency
Think about the old way of getting an NDA signed. You hunt for the right template, manually type in all the details, email it back and forth for review, and then cross your fingers hoping to get a physical signature back sometime this week. Every single step is a potential delay or a security risk.
Contract automation changes the entire game. With a platform like BoloSign, you can build out a library of pre-approved, ready-to-go templates for any scenario—whether it's an NDA for a new hire, a master service agreement for a big client, or a complex partnership deal.
This approach delivers a few immediate wins:
- Consistency: Every agreement starts from a compliant, lawyer-vetted template. No more worrying about someone using an old or unapproved version.
- Speed: You can spin up a new contract in seconds, with key details like names, dates, and project scopes filled in automatically.
- Visibility: A central dashboard gives you a live look at every document's status. You know exactly who has opened it, who's reviewing it, and who's signed.
AI-Powered Intelligence and Compliance
True efficiency is more than just sending documents faster. The best AI workflow automation tools now integrate AI contract review capabilities, giving you a powerful first line of defense against risk.
BoloSign’s AI can scan a clause of confidentiality to flag ambiguous or risky language, suggest stronger wording, and make sure you haven't missed any essential elements. It's like having a digital legal assistant that helps you negotiate better terms and sidestep common legal traps. If you want to go deeper on how this works, check out our guide to AI contract lifecycle management.
On top of that, compliance is baked right into the workflow. BoloSign is built to meet global standards like the ESIGN Act, eIDAS, HIPAA, and GDPR, so every eSignature is legally binding and secure. This is huge for organizations in highly regulated fields like healthcare or professional services where there’s zero room for error.
Industry Example: Picture a fast-growing staffing agency in the UAE that needs to onboard 50 contractors for a new project in Canada. Instead of a week of administrative chaos, the HR manager uses a BoloSign template to send out customized NDAs in one batch. From a single dashboard, they can see all the signatures roll in. A process that used to take days is now done in less than an hour, all while staying compliant with international privacy laws.
Unlocking Affordable, Unlimited Scale
Many businesses assume that this kind of enterprise-level contract automation is going to break the bank. Legacy providers often nickel-and-dime you with per-user or per-document fees, which gets expensive fast as your company grows. That pricing model basically forces you to ration a tool that everyone should be using.
BoloSign was built on a different philosophy. We offer unlimited documents, unlimited templates, and unlimited team members for one simple, fixed price. This makes our digital signing solution up to 90% more affordable than alternatives like DocuSign or PandaDoc.
This approach means you never have to think twice before sending an NDA or securing an agreement. Your entire organization—from sales and HR to procurement and legal—can sign PDFs online without ever worrying about hitting a usage cap. It’s all about making powerful contract automation accessible to every team that needs it.
Ready to stop chasing signatures and start automating your agreements? With BoloSign, you can create, send, and manage your confidentiality clauses with unmatched speed and security. Experience the difference an AI-powered, budget-friendly platform can make.
Start your 7-day free trial today and see how simple protecting your business secrets can be.

Paresh Deshmukh
Co-Founder, BoloForms
19 Dec, 2025
Take a Look at Our Featured Articles
These articles will guide you on how to simplify office work, boost your efficiency, and concentrate on expanding your business.